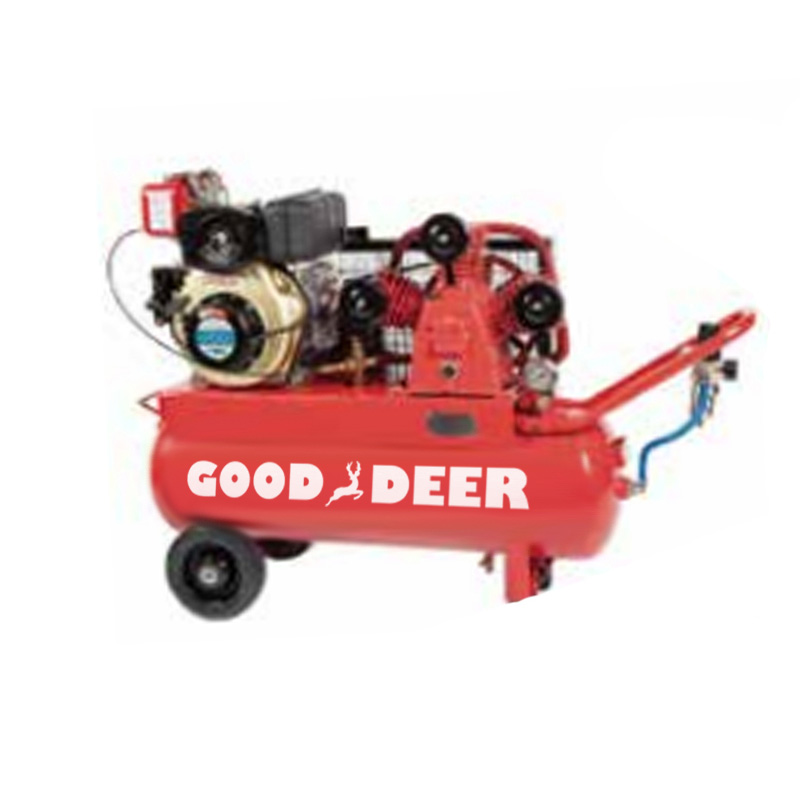
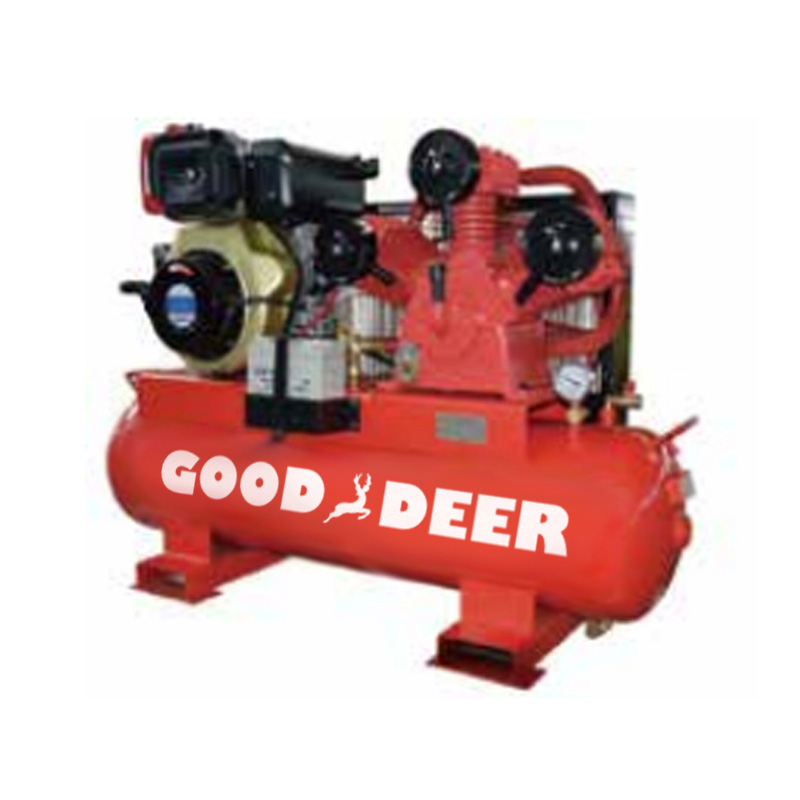
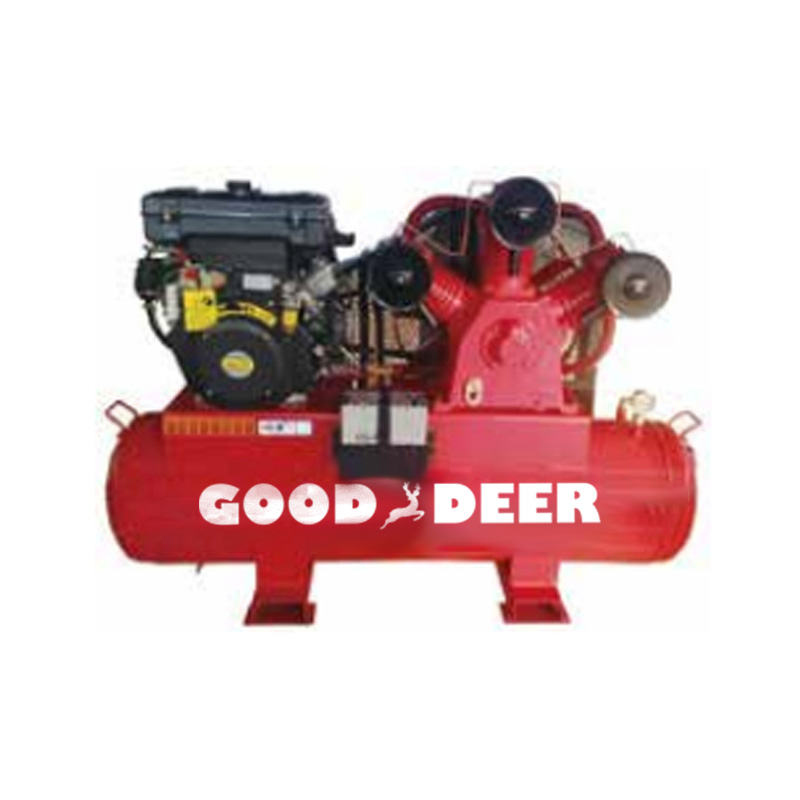
What Are the Common Faults and Solutions for Diesel Engine-Driven Piston Air Compressors?
Introduction to Diesel Engine-Driven Piston Air Compressors
Diesel engine-driven piston air compressors are widely used in industrial, agricultural, and construction applications. These compressors are highly valued for their ability to deliver high power output and operate in remote areas without electricity. However, like all machinery, they can experience faults over time that may affect their performance. Regular maintenance and early detection of issues are crucial for ensuring the efficient operation of these compressors. At Gooddeer, we offer reliable diesel engine-driven piston air compressors and provide expert guidance on how to troubleshoot and resolve common issues that may arise.
Engine Not Starting
One of the most common faults with diesel engine-driven piston air compressors is engine failure to start. This issue can be caused by several factors such as fuel system problems, a weak or dead battery, or faulty glow plugs. If the engine fails to start, begin by checking the fuel system for blockages or contamination. Ensure that the fuel tank is full and that the fuel is clean and free from impurities. A weak or dead battery can also prevent the engine from starting; replacing or recharging the battery may be necessary. Additionally, inspect the glow plugs as they are essential for starting a diesel engine, especially in cold conditions. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of faulty parts can help prevent this issue.
Loss of Air Pressure
A drop in air pressure is another common issue faced by diesel engine-driven piston air compressors. This problem is often caused by air leaks, valve malfunctions, or worn-out piston rings. If the compressor is not producing the expected air pressure, first inspect the air intake and exhaust valves for any leaks or blockages. Damaged valves can lead to air loss, reducing the compressor’s efficiency. Worn-out piston rings may also allow air to escape, lowering compression and air pressure. In such cases, replacing the piston rings can restore the compressor's performance. Regular checks for leaks and proper valve maintenance can help minimize this issue.
Overheating
Overheating is another common fault that can occur when using a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor, especially during prolonged operation. If the engine runs for an extended period without sufficient cooling, it may overheat, leading to performance issues or potential damage. Overheating can be caused by low coolant levels, clogged air filters, or insufficient ventilation. To address this problem, check the coolant level regularly and top it up as necessary. Ensure that the cooling system is functioning properly and that there are no blockages in the radiator. Dirty air filters can restrict airflow, causing the engine to overheat. Cleaning or replacing the air filters can prevent this issue and ensure proper engine cooling.
Excessive Fuel Consumption
High fuel consumption can indicate a problem with the fuel system or the engine itself. This issue is often caused by factors such as a clogged fuel filter, improper fuel type, or malfunctioning fuel injectors. If fuel consumption is higher than expected, check the fuel filter for any blockages and replace it if needed. Using the wrong type of diesel fuel can also affect the engine’s efficiency, so ensure that you are using high-quality fuel. Malfunctioning fuel injectors may need to be cleaned or replaced to restore optimal fuel efficiency. Regular maintenance and inspections of the fuel system can help prevent excessive fuel consumption.
Unusual Noises and Vibrations
Unusual noises or vibrations are often signs of mechanical issues with the diesel engine-driven piston air compressor. These can be caused by worn bearings, loose parts, or misalignment of the compressor components. If the compressor is producing abnormal sounds, inspect the bearings and other moving parts for wear or damage. Worn bearings can create friction, which results in noise and vibrations. If necessary, replace the bearings to eliminate the noise. Additionally, check all bolts and fasteners to ensure that they are properly tightened. Loose components can cause excessive vibrations, so tightening or replacing any damaged parts will restore smooth operation.
Oil Leaks
Oil leaks are another common fault in diesel engine-driven piston air compressors. Leaking oil can occur due to damaged seals, gaskets, or worn components. If you notice oil pooling around the engine, check the seals and gaskets for signs of wear or damage. Replace any worn or faulty seals to prevent oil from leaking out. Additionally, check the oil filter and oil drain plug to ensure that they are properly tightened. Tightening or replacing any damaged parts can help stop oil leaks and ensure proper lubrication of the engine, reducing the risk of damage.
Excessive Exhaust Smoke
Excessive exhaust smoke can indicate a problem with the combustion process. Black smoke typically suggests incomplete combustion, which could be caused by a clogged air filter, dirty fuel injectors, or an incorrect air-fuel mixture. To resolve this, check the air filter and clean or replace it if it is clogged. Clean or replace any dirty fuel injectors to improve fuel efficiency and combustion. If the engine is emitting blue or white smoke, it may indicate problems such as worn engine parts, burning oil, or coolant leakage. These issues require further investigation and repair to restore optimal engine performance.
Cold Weather Starting Issues
Cold weather can affect the performance of diesel engines, especially during the winter months. Thickened fuel, a weak battery, or faulty glow plugs can prevent the engine from starting in low temperatures. To ensure proper operation during cold weather, use winter-grade diesel fuel, which is less likely to thicken. If the battery is old or weak, consider replacing or recharging it. Glow plugs, which help start diesel engines in cold weather, should be checked and replaced if they are not functioning correctly. Maintaining the fuel system, battery, and glow plugs is essential to ensure reliable starting in cold conditions.
FAQ
Q: What maintenance is required for a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor?
A: Regular maintenance is essential to keep a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor running efficiently. Key tasks include checking and changing the oil, inspecting and replacing air filters, cleaning or replacing fuel filters, and ensuring that the coolant system is functioning properly. It’s also important to monitor the battery, check for oil leaks, and clean the compressor’s exterior regularly. Following the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule helps prolong the lifespan of the compressor and ensures reliable operation.
Q: How can I improve the fuel efficiency of my diesel engine-driven piston air compressor?
A: To improve the fuel efficiency of your diesel engine-driven piston air compressor, make sure the engine is well-maintained by keeping the fuel system clean and ensuring that the fuel injectors are in good condition. Regularly change the air and fuel filters to ensure proper airflow and fuel delivery. Additionally, operating the compressor at the recommended load capacity will prevent overuse of fuel. Proper storage and ensuring that the compressor is not exposed to extreme weather conditions can also help maintain its fuel efficiency.
Q: Can a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor be used in cold weather?
A: Diesel engine-driven piston air compressors can be used in cold weather, but special precautions should be taken. Using winter-grade diesel fuel prevents the fuel from thickening in low temperatures, which could cause the engine to have difficulty starting. Additionally, the battery may lose charge faster in cold conditions, so it’s essential to keep it well-maintained. To ensure optimal performance, use engine block heaters and check the glow plugs regularly to ensure smooth operation in freezing temperatures.
Q: What is the typical lifespan of a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor?
A: The lifespan of a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor depends on several factors, including the frequency of use, maintenance practices, and operating conditions. On average, with proper care and regular maintenance, these compressors can last between 10 to 15 years. Ensuring that the compressor is used within its specified limits and that regular servicing is performed can significantly extend its operational life.
Q: How do I troubleshoot low pressure in my diesel engine-driven piston air compressor?
A: Low pressure in a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor can result from several issues such as air leaks, faulty valves, or worn piston rings. Begin by checking for any visible air leaks in the intake or exhaust systems and ensuring that all seals are intact. If the valves are malfunctioning, they may need to be cleaned or replaced. Additionally, worn piston rings can reduce the engine’s ability to generate proper air pressure, and replacing the rings will help restore performance. Regularly monitoring pressure levels can help identify such issues early.
Q: What are the advantages of using a diesel engine-driven piston air compressor over an electric model?
A: Diesel engine-driven piston air compressors offer the advantage of mobility and independence from the electrical grid, making them ideal for use in remote or outdoor environments where power sources are unavailable. They also tend to provide higher power outputs for heavy-duty tasks such as construction, mining, and large-scale agricultural operations. Additionally, diesel engines tend to have longer run times compared to electric models, which makes them suitable for continuous operation in demanding conditions.